Melasma is a form of hyperpigmentation on the face. Genetics, hormones, and sun exposure are the major causes of melasma.
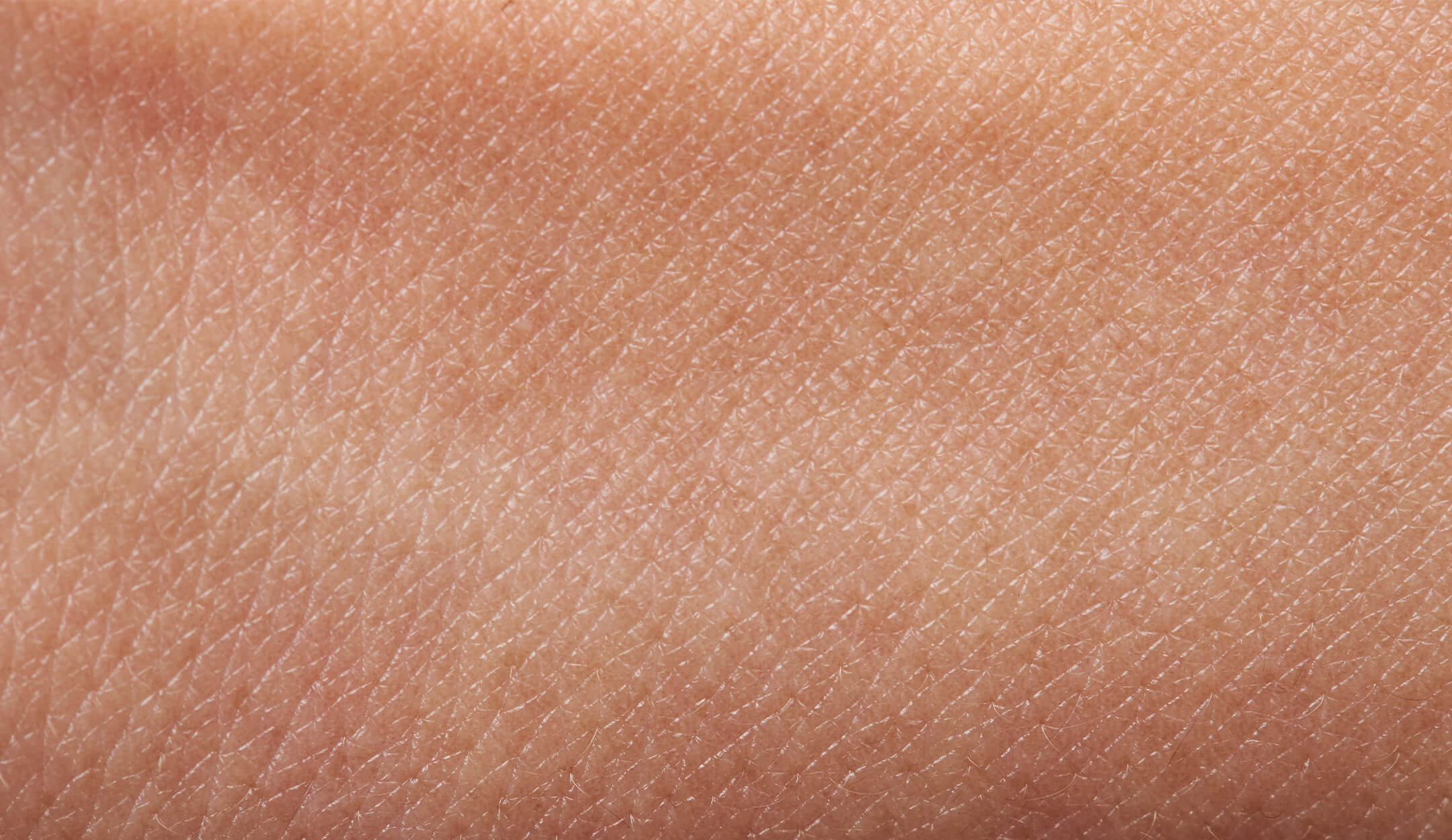
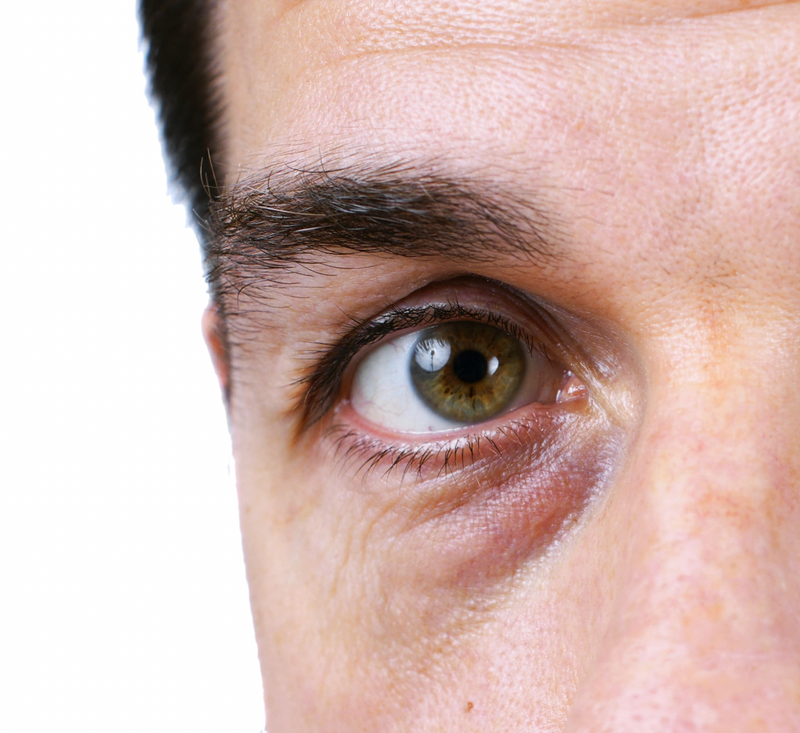
Melasma is characterized by dark patches of skin on the face. These patches result when melanocytes, a type of skin cell that produces skin pigment, become overactive producing extra pigment that deposits in the skin.
The most common cause of melasma is sun exposure, but hormone spikes from oral contraceptive pills (birth control) and during pregnancy can exacerbate the condition.
Melasma is one of the most challenging conditions to treat in dermatology and often relapses despite adequate treatment. The first-line treatment for melasma is to use a tinted sunscreen with iron oxides to prevent worsening hyperpigmentation. Ingredients such as hydroquinone, arbutin, kojic acid, retinoids, and vitamin C can all be used to treat melasma once it forms.